There are many different types of owls that can be found in Minnesota. Some of the most common include the barred owl, the great horned owl, and the snowy owl. Each type of owl has its own unique characteristics and habits. In this blog post, we will discuss the different types of owls that can be found in Minnesota, as well as their habits and characteristics. We will also provide some tips for spotting these amazing creatures!
Only reputable sources and an Ornithologist were consulted to verify the data.
Most Common Owls in Minnesota
Northern Hawk Owl
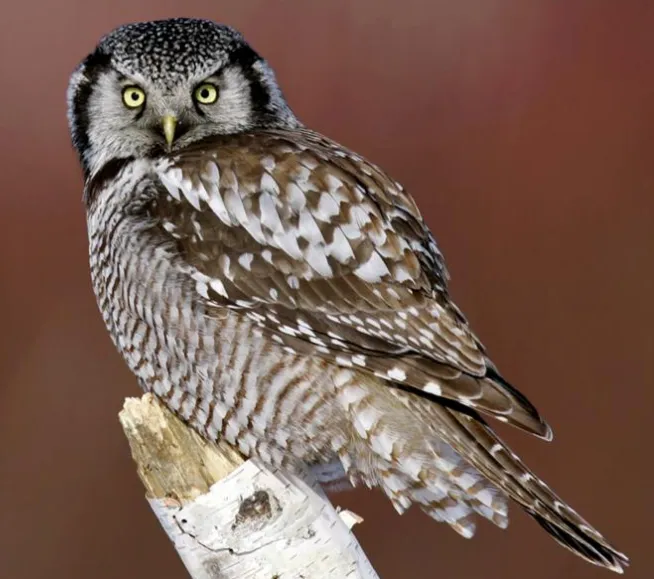

The Northern Hawk Owl is a medium-sized owl with broad wings and a long tail. They are one of the few owls that are active during the day, although they will also hunt at night. Their diet consists mostly of small rodents and birds.
These owls can be found in woodlands, forests, and tundra habitats across northern North America. In Minnesota, they are most commonly found in the northern and central parts of the state.
If you’re lucky enough to see a Northern Hawk Owl, you’ll likely hear their distinctive call first. They make a repetitive “kee-yah” sound that is often described as sounding like a screech owl on steroids.
These owls are also known for their loud screams, which they use to communicate with each other.
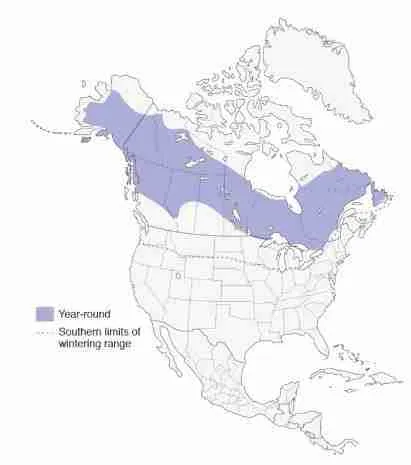
Great Gray Owl
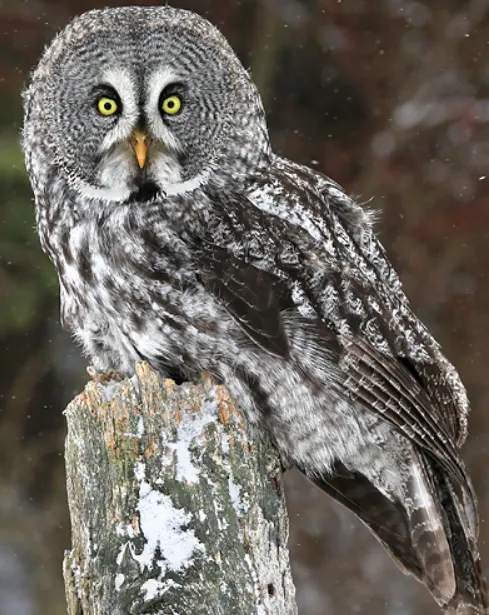

The Great Gray Owl is one of the largest owls in North America, with a body length of up to 28 inches. It has a large, round head, and yellow eyes. Its wingspan can reach up to 60 inches.
The Great Gray Owl is mostly grey, with some brownish feathers on its back and head. It has a white facial disk, with a black border. Its belly is white, with dark brown streaks.
The Great Gray Owl is found in northern forests of North America, Europe, and Asia. In North America, it is found in Alaska, Canada, and the northern United States. It prefers to live in coniferous forests near wetlands.
The Great Gray Owl is a nocturnal bird, meaning it is active at night. It hunts by perching on a tree or pole, and waiting for prey to come close. It also hunts by flying low over the ground, and listening for the sounds of small animals moving.
When it hears an animal, it swoops down and grabs it with its talons. The Great Gray Owl eats mostly small mammals, such as mice, voles, and lemmings. It will also eat birds, snakes, and insects.
The Great Gray Owl nests in tree cavities, or in nest boxes made for owls. It lays two to six eggs per clutch. The female incubates the eggs for about 30 days. The young owls leave the nest after about six weeks. Both parents help to raise the young.
The Great Gray Owl is a protected species in Canada and the United States. Hunting of this owl is not allowed.

Short-eared Owls

Short-eared Owls are one of the most widespread owl species in the world. They are found on every continent except Antarctica and prefer open habitats such as grasslands, meadows, tundra, and marshes. In North America, they are most common in the northern Great Plains and Great Lakes region.
Short-eared Owls are relatively small owls, measuring about 13-16 inches in length and having a wingspan of approximately 32-40 inches. They are brownish-gray in color with mottled white spots on their back and wings.
The chest and belly are pale with dark streaks. Short-eared Owls have large, round heads with no ear tufts. Their eyes are yellow and their beaks are black.
Short-eared Owls are mostly active at night, although they may also be seen hunting during the day. They hunt by flying low over the ground in search of small mammals such as voles, mice, and lemmings. When prey is spotted, the owl swoops down and grabs it with its sharp talons. Short-eared Owls will also eat birds, reptiles, and insects.
These owls do not build their own nests. Instead, they use the abandoned nests of other birds such as hawks, crows, and squirrels. Short-eared Owls typically lay between three and seven eggs at a time.
Short-eared Owls are relatively easy to spot if you know where to look. They often perch on fence posts or low branches in open areas. During the day, they roost in dense vegetation to avoid predators. If you see an owl perched in an open area during the day, it is likely a Short-eared Owl.
These owls are also often seen flying low over the ground in search of prey. If you hear an owl hooting at night, it is probably a Short-eared Owl. The call of a Short-eared Owl sounds like “kow-kow-kow” or “quank-quank-quank.”

Great Horned Owl
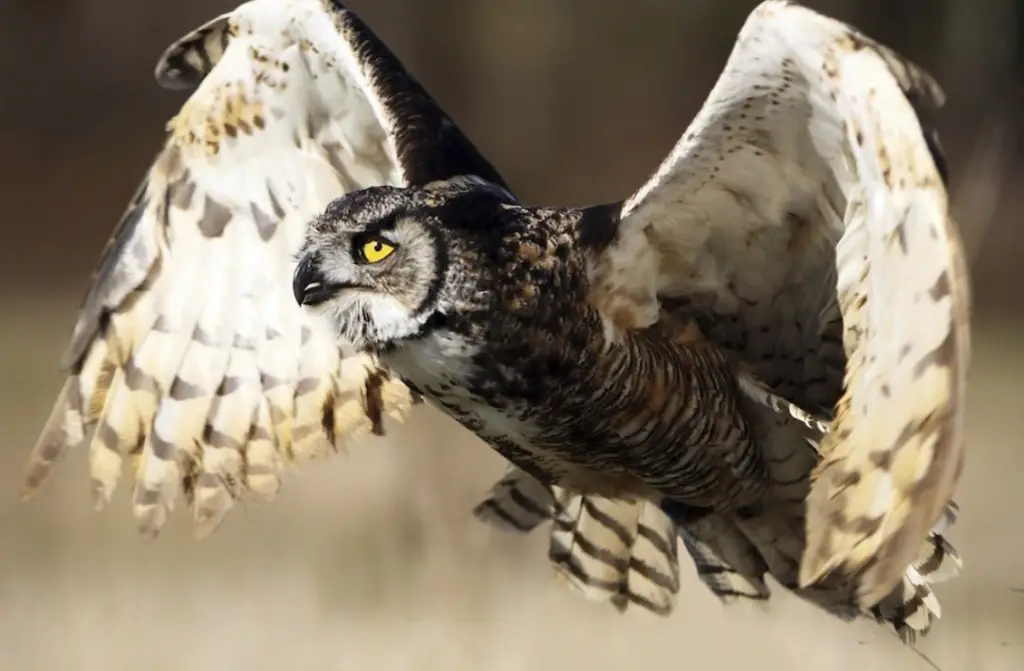

The Great Horned Owl is a large owl with prominent ear tufts. It has a large head and yellow eyes. The Great Horned Owl is brown with white streaks on its chest. It has a wingspan of up to five feet. The Great Horned Owl is found in North and South America.
In Minnesota, the Great Horned Owl is found in the northern part of the state. The Great Horned Owl feeds on small mammals, birds, and reptiles. It hunts at night and uses its sharp claws and beak to kill its prey. The Great Horned Owl nests in trees and lays two to three eggs per clutch.
The Great Horned Owl is a protected species in Minnesota.
If you see a Great Horned Owl in Minnesota, please report it to the DNR. This majestic creature is an important part of our state’s ecosystem and we need to do everything we can to protect it.

Burrowing Owls
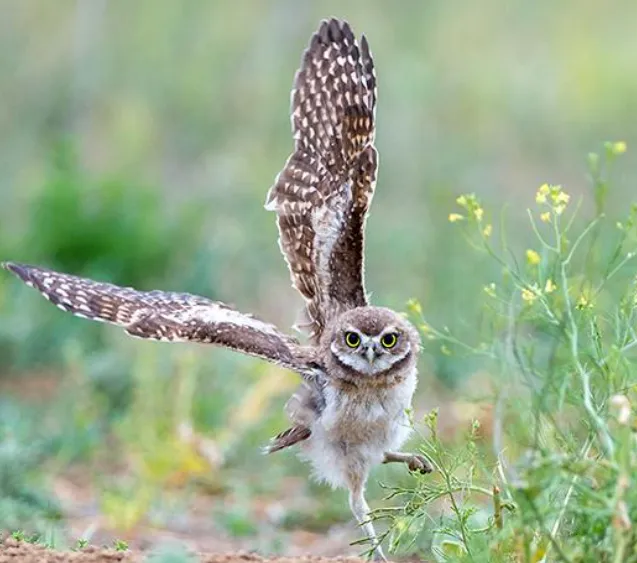

As Minnesota’s only resident owl that lives primarily on the ground, the burrowing owl is a fairly distinctive bird.
And while it’s true that many animals are more active and easier to see during the daytime, this nocturnal creature is one of the few that can actually be easier to find when the sun is up. Here are a few tips on how to identify and find burrowing owls in Minnesota.
One of the most reliable ways to spot a burrowing owl is by its call, which sounds something like a loud, harsh “k-r-r-ick” or “k-r-eek.” Another telltale sign is the bird’s behavior: they often perch on top of a fence post or other elevated surface, and they have a habit of bobbing their heads up and down.
And of course, the easiest way to find a burrowing owl is to look for its home: a small hole in the ground that it uses for nesting and roosting.
If you’re lucky enough to spot a burrowing owl, you can also try to get a good look at its plumage. The bird is mostly brown and white, with long legs and a relatively small body.
Its head is round and lacks the ear tufts that are characteristic of other owls, and its eyes are yellow. Juvenile birds may have more mottled plumage, and they may also have blue eyes.

Related post: Types of Owls in California
Snowy Owl
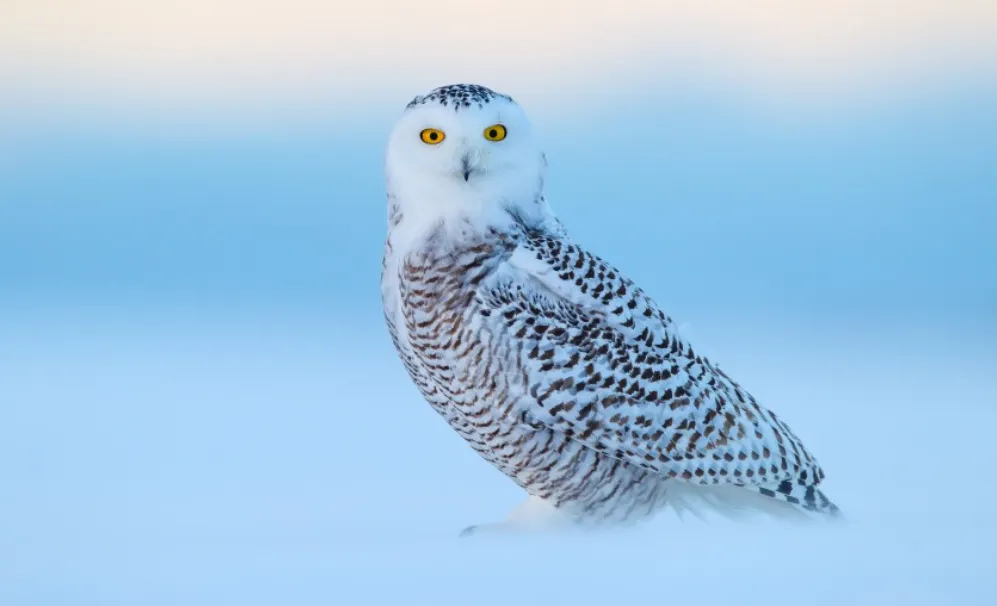

Habitat: Snowy owls live in the Arctic tundra. They are also found in northern Europe and Asia.
Nesting: Snowy owls nest on the ground, usually on a hillock or hummock. The nest is a scrape in the ground lined with feathers and down.
Eggs: Snowy owls lay from three to eleven eggs.
Behavior: Snowy owls are mostly active at night. During the day, they perch on a stump, fence post, or other elevated objects. They also hunt during the day if necessary. Snowy owls are excellent hunters and can take down prey much larger than themselves.
Identifying Characteristics: Snowy owls are large, white owls with black bars on their wings. They have a round head with yellow eyes. Their feet are covered in feathers to help keep them warm in the cold climates where they live. Snowy owls can also be identified by their call, which is a low, hooting sound.

Northern Saw-whet Owl

The Northern Saw-whet Owl is a small owl with a large head and round body. It has a white face with black eyes and a dark brown or black beak. Its back is brown or gray with white spots, and its belly is white. It has long legs and talons. Its wings are short and rounded.
This owl is found in the forests of North America. It nests in trees, stumps, or logs. It hunts at night for small mammals, such as mice and voles. In winter, it may eat birds.
The Northern Saw-whet Owl is active at night. During the day, it roosts on a tree branch or in a nest. It is a good flier and can be seen flying low over the ground or among trees.
This owl can be found in Minnesota during the breeding season. It nests in forests, typically near lakes or wetlands. In winter, it may be found in southern Minnesota.
To find this owl, look for its distinctive call. It also can be found roosting during the day in trees or on fence posts. Look for its white face and black eyes. If you see this owl, please report it to the Minnesota Breeding Bird Atlas.

Long-eared Owl
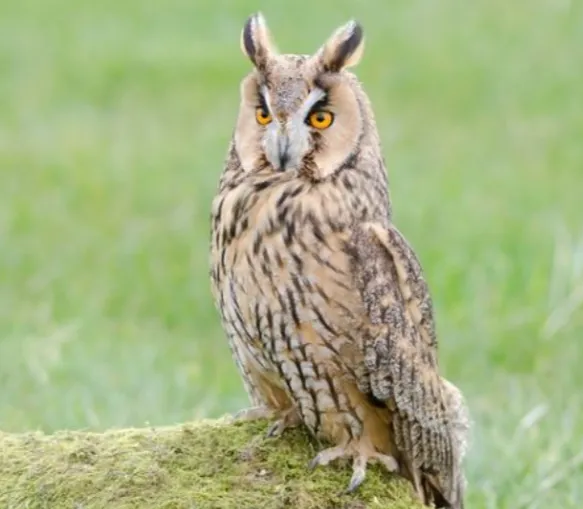

The long-eared owl is a medium-sized owl with large, prominent ear tufts. It has yellow eyes and a gray beak. The body is gray with brown streaks. The wings are black with white spots. The tail is long and black with white stripes. The legs are long and gray.
This owl is found in woodlands, forests, and wetlands. It nests in trees. The female lays two to six eggs. The young owls fledge at about eight weeks of age.
The long-eared owl is active at night. It hunts small mammals, such as mice and voles. It also eats birds, insects, and reptiles.
This owl is found in North America, Europe, and Asia. In North America, it is found in Canada and the United States. It is a year-round resident of Minnesota.
Long-eared owls are relatively easy to identify. However, they can be confused with other species of owls. If you see an owl with ear tufts, look for the following characteristics to be sure it is a long-eared owl: yellow eyes, gray beak, streaked body, black wings with white spots, long tail with white stripes, and long legs. If you are still unsure, listen for its call.

Eastern Screech Owl
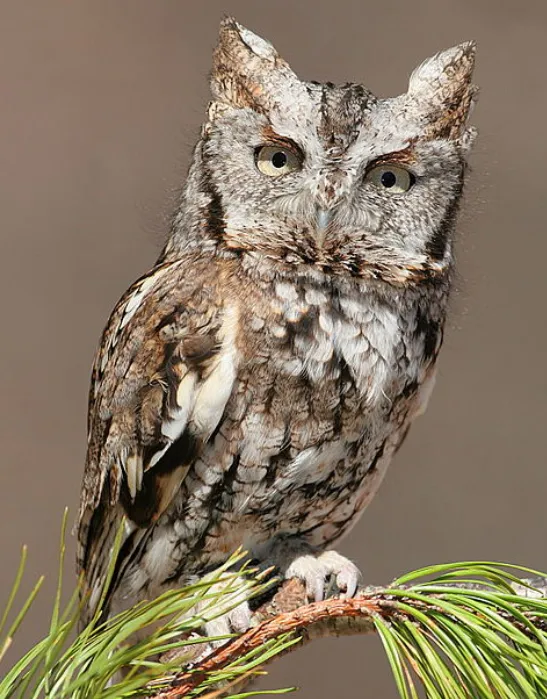

The Eastern screech owl is a small owl with large, ear-like tufts of feathers. It has a grayish-brown body with streaks of darker brown. Its belly is lighter in color with vertical bars. It has yellow eyes and a black beak. The Eastern screech owl can be found in wooded areas of eastern North America. It feeds on small mammals, birds, and insects.
The Eastern screech owl is nocturnal, meaning it is most active at night. During the day, it roosts in tree cavities or nest boxes. It nests in tree cavities or nest boxes lined with leaves and grass. Eastern screech owls are non-migratory, meaning they stay in the same area year-round.
If you’re lucky enough to spot an Eastern screech owl, you’ll likely see it sitting on a tree branch or hunting from a perch. These owls are expert hunters and can capture their prey in complete darkness. If you hear a high-pitched trill coming from the woods, it’s probably an Eastern screech owl.
These owls use this call to communicate with each other. Eastern screech owls are fascinating creatures and it’s always a treat to see one in the wild!

American Barn Owl
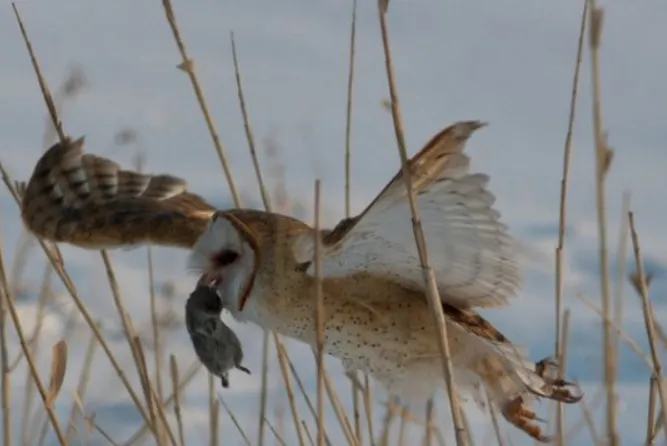

The American Barn Owl is a medium-sized owl with a large, round head and no ear tufts. It has a black beak, dark eyes, and white facial disks surrounded by a dark rim. The upper parts are pale grayish brown, heavily streaked with black.
The underparts are white with heavy grayish brown streaks. The wings are long and rounded. The tail is short and square.
This owl gets its name from the fact that it often nests in old barns, abandoned buildings, and other man-made structures. It will also nest in cliffs, caves, trees, and other natural sites.
The American Barn Owl is found throughout North America. It is most common in the western United States, but it also occurs in the eastern states, as well as in Canada and Mexico.
The American Barn Owl is active at night, when it hunts for rodents, such as mice and rats. It uses its sharp claws and beak to kill its prey. The owl then swallows the prey whole.
The American Barn Owl is a cavity nester, meaning it nests in holes in trees or other structures. The female lays two to six eggs in each nest. The young owls fledge, or leave the nest, at about seven weeks of age.

Barred Owl

The barred owl is a large owl with a rounded head and no ear tufts. It has dark brown eyes and a black beak. The upperparts are grayish-brown with white streaks. The underparts are pale with dark streaks. The wings are long and broad. The tail is short and square.
The barred owl is found in forests across North America. It is a nocturnal bird and is most active at night. It hunts small mammals, birds, and reptiles. The barred owl is territorial and will defend its territory from other owls.
The barred owl is a monogamous bird. The female lays two to four eggs in a nest made of sticks. The nest is usually in a tree cavity. Both parents help to raise the young. The young owls leave the nest after about six weeks.
The lifespan of a barred owl is up to 15 years in the wild and up to 28 years in captivity.
The barred owl is not currently considered threatened or endangered.

Barn Owl
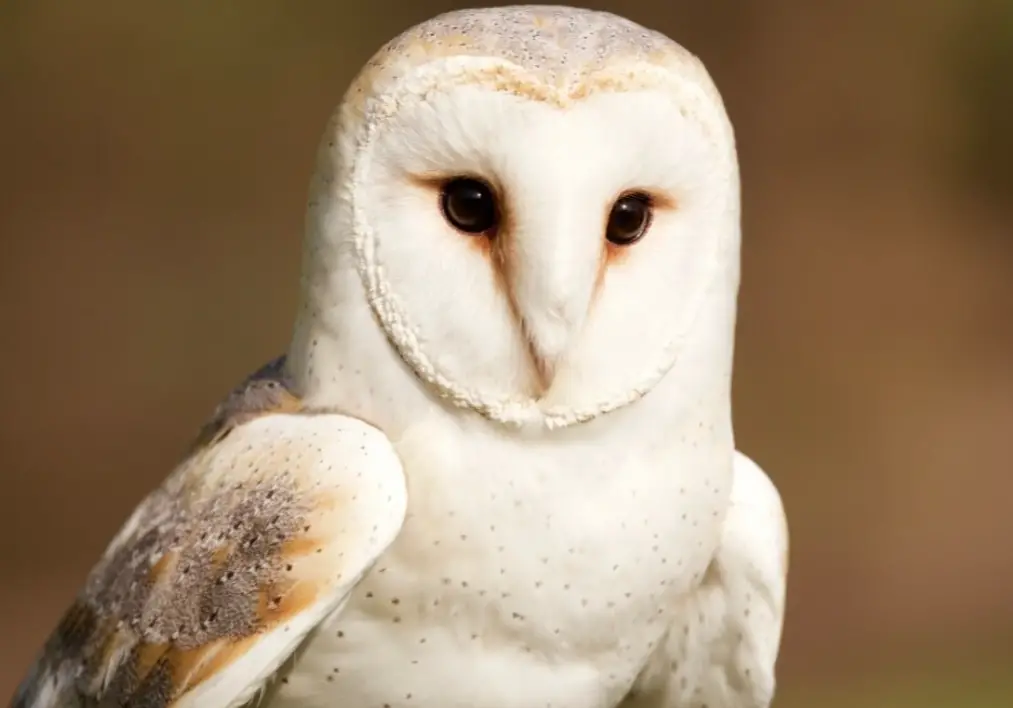

The Barn Owl is a medium-sized owl with a large, round head and no ear tufts. It has a white face with black eyes and a hooked beak. The upperparts are brown with white spots, while the underparts are pale with brown streaks. This owl gets its name from its habit of nesting in old barns and other buildings.
Barn Owls are found in open habitats such as fields, meadows, and prairies. They hunt for small mammals such as mice and voles. Barn Owls are nocturnal, meaning they are most active at night. During the day, they roost in trees or on the ground in dense vegetation.
If you see a Barn Owl, you can report it to your local Audubon Society chapter or the Minnesota DNR. When reporting an owl sighting, please include the date, time, and location of the sighting, as well as any other information that might be helpful. With your help, we can learn more about these fascinating creatures!
The best time to see a Barn Owl in Minnesota is during the breeding season, which runs from April to August. During this time, males and females can often be seen hunting together. After the young owls fledge, they disperse to find their own territories.

Are owls common in Minnesota?
Yes, owls are common in Minnesota. There are two species of owls that are particularly common in the state: the Barn Owl and the Barred Owl. Both of these owls are nocturnal, meaning they are most active at night.
Where are owls found in Minnesota?
Owls are found throughout the state of Minnesota. They are most common in forests, but they can also be found in open habitats such as fields and meadows.
Are owls rare in Minnesota?
No, owls are not rare in Minnesota.
Are owls good to have around your house?
There is no definitive answer to this question. Some people believe that owls are good to have around your house because they can help to control rodent populations. Others believe that owls are bad to have around your house because they might prey on pets or small children.

An avid ornithologist, zoologist and biologist with an unwavering passion for birds and wild animals.
Dr. Wilson’s journey in ornithology began in childhood and led him to obtain a Ph.D. in Ornithology from the prestigious Avian Research Institute. He has worked closely with renowned experts in the field and conducted extensive research and field studies globally.

