The data was obtained only from trustworthy sources, and it was double-checked with an Ornithologist.
Wisconsin is a great place to see owls in the wild. There are many different types of owls that can be found in the state, including the barred owl, the great horned owl, and the eastern screech owl. In this blog post, we will discuss the different types of owls that can be found in Wisconsin, as well as where you can find them. We will also provide some tips on how to spot owls in the wild. So if you’re interested in learning more about owls in Wisconsin, keep reading!
Most Common Owls in Wisconsin
Barred Owls

The Barred Owl is a large bird, with a body length of 18 to 20 inches. The wingspan can range from 36 to 42 inches. The owl gets its name from the horizontal stripes on its chest and belly, which look like bars.
The head is round, with no ear tufts. The eyes are dark brown and the beak is black. The Barred Owl is found in wooded areas throughout Wisconsin. It nests in trees, and will also use man-made structures such as nest boxes.
The Barred Owl is active at night and uses its powerful sense of hearing to locate prey. It hunts small mammals such as mice, voles, and squirrels. The owl uses its sharp claws and beak to kill its prey. Barred Owls will also eat birds, reptiles, and insects.
During the breeding season, the male Barred Owl will call out “who-cooks-for-you” to attract a mate. The female will respond with a hooting call. The pair will mate for life and will use the same nest site year after year.
The female will lay two to four eggs in a nest made of sticks and leaves. Both parents help to incubate the eggs, which hatch after about 28 days. The young owls are able to fly at about six weeks of age.

Great Horned Owls

The Great Horned Owl is a large bird of prey that can be found in wooded areas throughout Wisconsin. These owls are easily identified by their large size, distinctive plumage, and loud call. Great Horned Owls are mostly active at night, so they are often seen roosting during the day.
These birds typically nest in tree cavities, but will also use man-made structures such as nest boxes. Great Horned Owls typically prey on small mammals such as rabbits and mice, but they will also eat birds, reptiles, and invertebrates.

Northern Hawk Owl
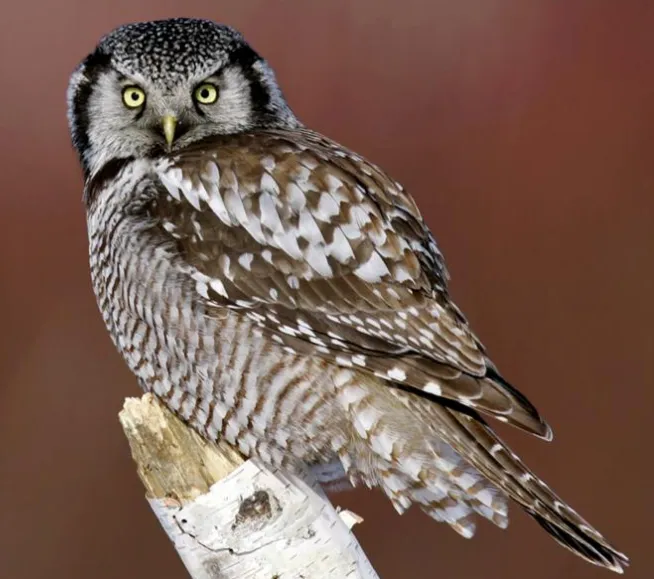

The Northern Hawk Owl is a medium-sized owl with a large head and long, pointed wings. The upperparts are brown with white spots, and the underparts are pale with dark streaks. The eyes are yellow, and the beak is black.
Northern Hawk Owls are found in forests of the northern United States and Canada. In Wisconsin, they are most often seen in the northern and central parts of the state.
Northern Hawk Owls hunt during the day, perching on branches or poles and watching for prey.
They eat small mammals such as mice, voles, and squirrels. Northern Hawk Owls nest in trees, often using abandoned nests of other birds such as hawks, crows, or squirrels.
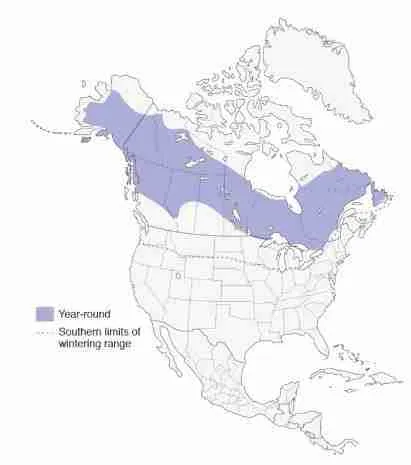
Long-eared Owls
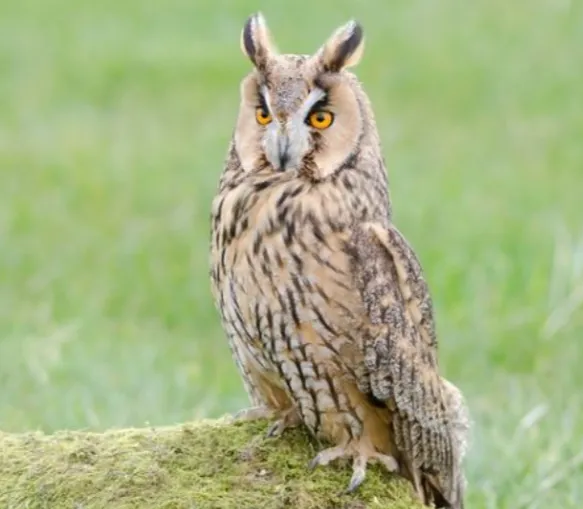

Long-eared Owls are a medium sized owl with brown and white mottled plumage. The “long ears” for which they are named are actually tufts of feathers that extend from the sides of their heads.
These tufts may be raised or lowered at the owls’ discretion, and are thought to play a role in communication. Long-eared Owls are found in wooded areas across North America, Europe, and Asia.
In Wisconsin, Long-eared Owls are most often found in the northern part of the state. They typically nest in trees, using old nests built by other birds such as crows or squirrels. These owls do not build their own nests.
Long-eared Owls are nocturnal hunters, and will prey on small mammals such as mice, voles, and shrews.
If you are lucky enough to see a Long-eared Owl in the wild, you can identify it by its long ear tufts, mottled plumage, and yellow eyes. These owls are relatively silent, but you may hear a faint hooting sound if they are nearby.

Great Gray Owl
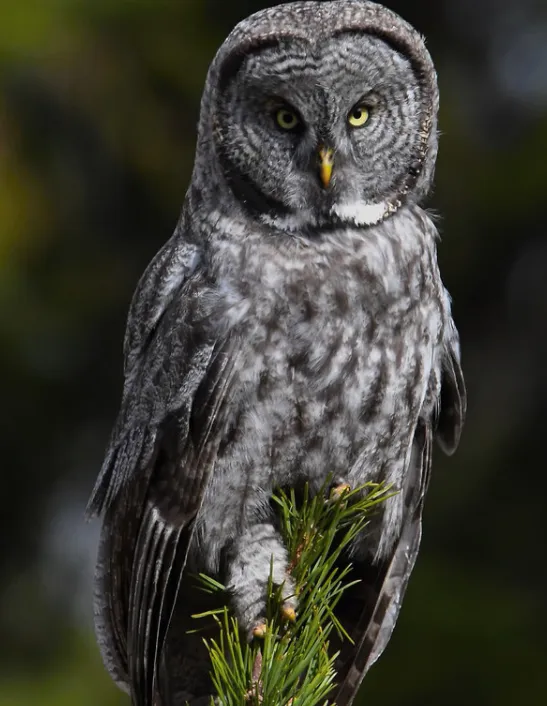

The Great Gray Owl is a very large owl, with a body length of up to 27 inches. They have a wingspan of up to 60 inches, and can weigh up to three pounds. The females are usually larger than the males.
These owls are gray in color, with some brownish mottling on their back and breast. They have a large, round head, and yellow eyes. Their beak is black, and they have ear tufts. Great Gray Owls are silent flyers, and can hunt by sound alone.
These owls inhabit the northern forests of North America. In Wisconsin, they are found in the northern part of the state, in areas with coniferous trees.
They nest in trees, and will often use old nests of other birds, such as hawks or crows. Great Gray Owls hunt small mammals, such as mice, voles, and shrews. They will also eat birds, reptiles, and insects.

Snowy Owl
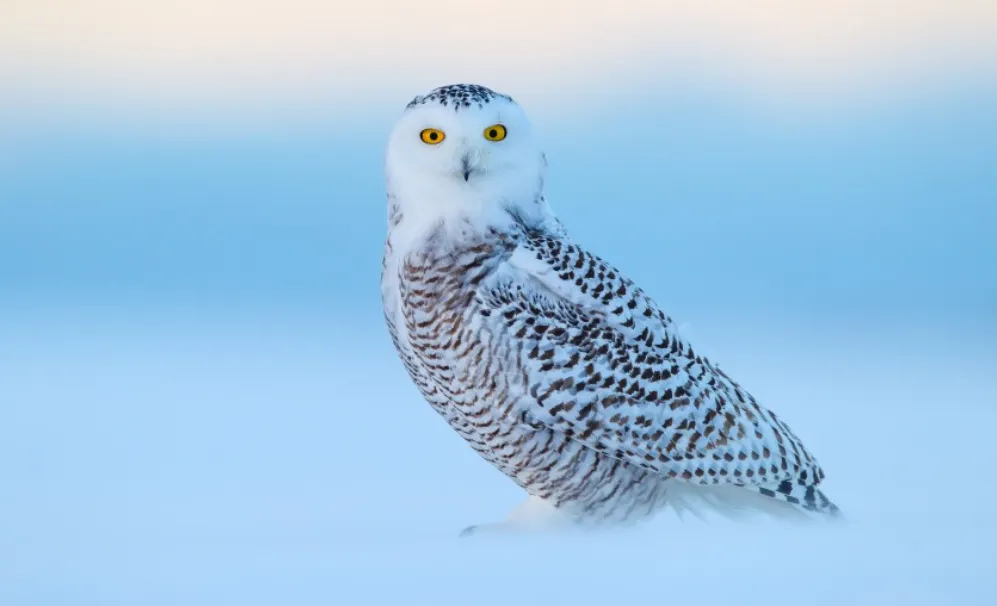

The Snowy Owl is a large, white owl of the true owl family. Males are almost all white, while females have more flecks of black feathers. Juvenile owls are heavily mottled with dark brown and gray.
The Snowy Owl’s head is round with a flat face and no ear tufts. It has bright yellow eyes and a black beak. The owl’s wings are long and broad, and its tail is relatively short.
The Snowy Owl is a bird of the northernmost parts of the world. In North America, it breeds mostly in Alaska and northern Canada. It is also found in Europe, Asia, and Greenland.
In winter, the Snowy Owl may be seen as far south as the Great Lakes, southern Canada, and even northern parts of the United States.
The Snowy Owl is an opportunistic feeder that will eat a wide variety of prey, including voles, lemmings, mice, rabbits, squirrels, and birds up to the size of a duck. The owl may also eat carrion.
In the winter, when its preferred prey is buried under snow, the Snowy Owl will hunt by day as well as by night.

Barn Owl
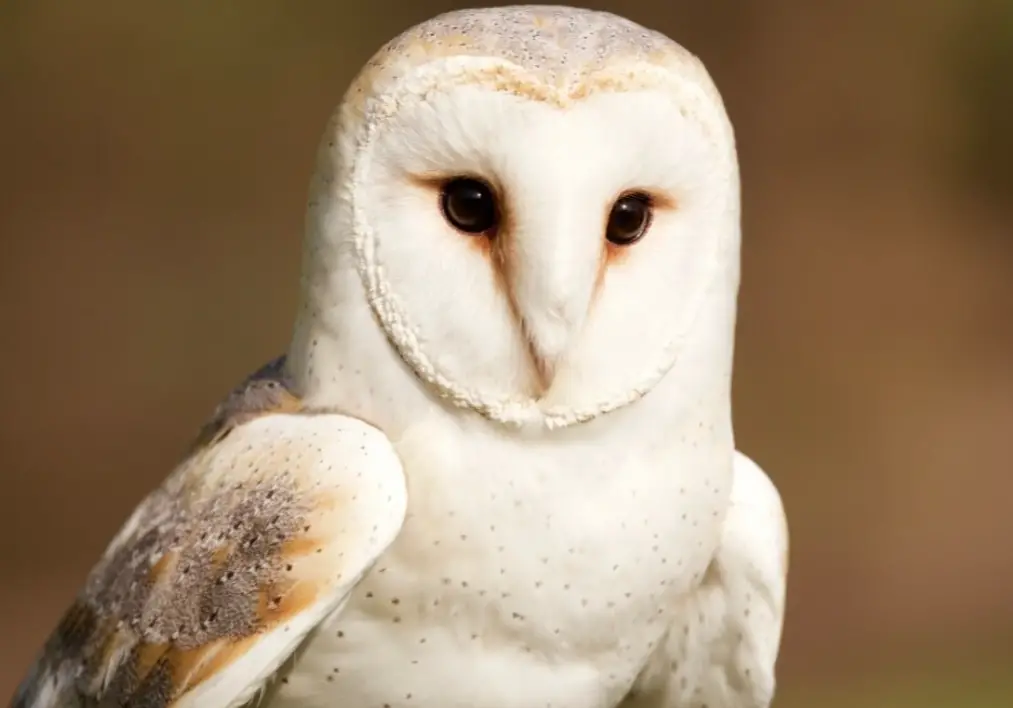

The barn owl is a medium-sized owl with a large, round head and no ear tufts. It has a white face with black eyes and a black beak. The upperparts are brown with white spots, and the underparts are pale with dark streaks.
The wings are long and rounded, and the tail is short. Females and males look alike. Juveniles are browner than adults and have more streaks on their undersides.
The barn owl is found in open areas such as farmland, pastureland, and grasslands. It nests in trees, barns, and other structures. The female lays two to six white eggs in a nest of straw and feathers.
The barn owl hunts at night, using its sharp eyesight and hearing to locate prey. It eats small mammals such as voles, mice, and shrews. The barn owl is found in Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australia. In North America, it is found in the United States and Mexico.

Related post: Types of Owls in Arizona
Eastern Screech Owls
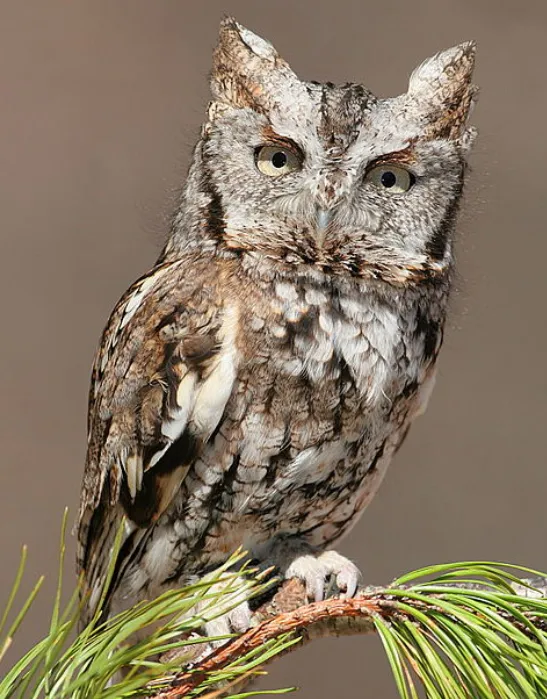

The Eastern Screech Owl is a small owl with large, round head and ear tufts. It has a gray-brown body with streaks of rust-brown on the breast and back. The eyes are yellow-orange. This owl is found in woodlands, forests, and urban areas across eastern North America.
The Eastern Screech Owl is a nocturnal bird, meaning it is most active at night. During the day, you can find this owl roosting in trees, often close to the trunk. It will sometimes use old woodpecker holes as nesting sites.
This owl hunts small mammals such as mice and shrews. It will also eat insects, frogs, and reptiles.
To attract an Eastern Screech Owl to your backyard, you can put up a nest box or roosting platform. This owl does not build its own nest, so it will use whatever cavity it can find. You can also provide this owl with a perch near some dense foliage where it can hide during the day.

Short-eared Owls

Short-eared owls are one of the most widespread owl species in the world. In Wisconsin, they can be found in nearly every county. Short-eared owls are medium-sized owls with ear tufts that are usually not visible.
They have yellow eyes and a brownish body with streaks of white or buff. The underparts are pale with dark streaks. The wings and tail are brown with white bars. Short-eared owls are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, wetlands, grasslands, and even tundra.
During the day, they perch on trees or poles, sometimes using their long legs to stand on top of dead leaves or snow. At night, they hunt for small mammals, such as mice, voles, and shrews. Short-eared owls are relatively easy to spot in the winter when they are often the only owl species active during the day.

Northern Saw-whet Owl

The Northern Saw-whet Owl is a small owl with big eyes. It has a round head with no ear tufts. The upperparts are brown with white spots, while the underparts are pale with heavy brown streaks.
This owl gets its name from its call, which sounds like “to-wit to-wit to-woo.”
The Northern Saw-whet Owl is found in forests across Canada and the northern United States. In Wisconsin, it is most likely to be found in the northern part of the state.
This owl hunts at night, using its sharp claws and beak to kill small mammals such as mice and voles. It sometimes hides its prey in a tree cavity or nest to eat later.

Boreal Owl
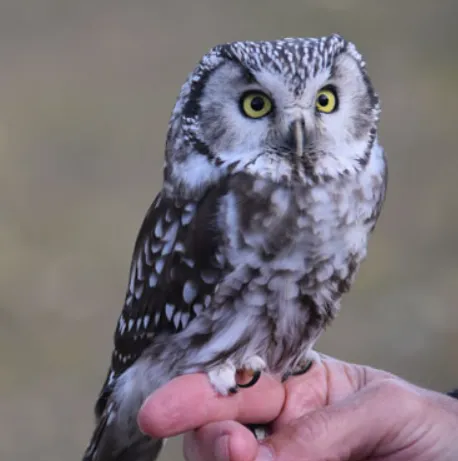

Boreal Owls are small to medium-sized owls with long, rounded wings and short tail. They have large, round heads with yellow eyes and no ear tufts. Their upper parts are brownish-gray with white spots, and their underparts are pale with dark streaks. Boreal Owls hunt from perches, and they eat small mammals, birds, and insects. In Wisconsin, they are most often found in the northern forests.
To identify a Boreal Owl, look for these characteristics:
- Small to medium size
- Long, rounded wings
- Short tail
- Large, round head
- Yellow eyes
- No ear tufts
- Brownish-gray upperparts
- White spots on upperparts
- Pale underparts
- Dark streaks on underparts
When you see a Boreal Owl, it is likely to be doing one of these activities:
- Hunting from a perch
- Eating small mammals, birds, or insects

Burrowing Owls

Burrowing owls are small, stocky owls with long legs. They have large heads and eyes, and a hooked bill. Their plumage is brown and white, with dark streaks on the breast. The female burrowing owl is usually larger than the male.
Burrowing owls get their name from their habit of living in burrows that they excavate themselves, or that are abandoned by other animals such as prairie dogs. These owls hunt during the day, and at night roost on perches near the entrances to their burrows.
During the breeding season, male burrowing owls perform a courtship display in which they bow, call, and flap their wings. The female will then select a mate and the pair will excavate a new burrow together. They will also use abandoned burrows of other animals.
Burrowing owls typically lay between four and eight eggs, which are incubated by the female for about 28 days. The young owls fledge (grow their feathers and learn to fly) at about seven weeks of age, but they remain dependent on their parents for food for several more weeks.

American Barn Owl
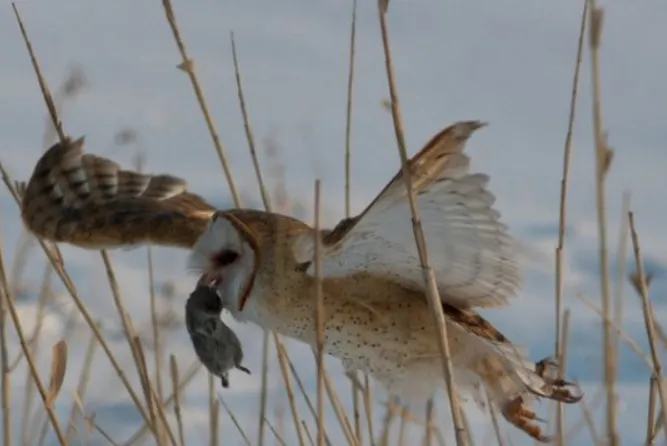

The American Barn Owl is a medium-sized owl with a large, rounded head and no ear tufts. Its eyes are dark brown and its bill is pale. The adult has white facial disks with a black border, and its upperparts are reddish brown with black streaks. The underparts are whitish with heavy black streaking.
This owl gets its name from its habit of roosting and nesting in barns and other outbuildings. It will also use abandoned buildings, caves, culverts, rock crevices, tree cavities, and old nests of other birds. The American Barn Owl is found throughout the United States. It is most common in the Great Plains and the West.
The American Barn Owl is a nocturnal predator. It hunts over open country, using its sharp hearing to locate prey by sound. Its diet consists of small mammals, such as voles, mice, and shrews. The American Barn Owl nests in tree cavities, cliffs, and abandoned buildings.
It often uses the same nest site for many years. This owl is monogamous and usually mates for life. Both parents help to raise the young. The female lays two to six eggs, which hatch in about a month. The young owls leave the nest after about seven weeks.
The American Barn Owl is not currently considered endangered, but its numbers have declined in recent years. This decline is likely due to the loss of suitable habitats, such as old barns and other outbuildings. Pesticides may also be a factor in the decline of this owl.

Why is there an owl in my backyard?
The most likely answer is that there is an owl in your backyard because it is looking for food. Owls are predators, and they hunt small mammals such as voles, mice, and shrews. If you have a lot of trees in your backyard, it may be attracting owls looking for a place to nest.
How do I know what kind of owl is in my yard?
There are several ways to determine what kind of owl is in your yard. One way is to look at the size of the bird. The Great Horned Owl is one of the largest owls in Wisconsin, and it can be easily distinguished by its large size and distinctive plumage.
Another way to identify an owl is by its call. The Barred Owl is named for the horizontal stripes on its chest and belly, which look like bars. This owl makes a who-cooks-for-you call that is distinctive and easy to recognize.
Finally, you can also identify an owl by its hunting habits. The Northern Hawk Owl is a day hunter, and it often perches on branches or poles in search of prey.
What owls are in Wisconsin?
The most common owls in Wisconsin are the Barred Owl, the Great Horned Owl, and the Northern Hawk Owl. These owls can be distinguished by their size, plumage, and hunting habits.

An avid ornithologist, zoologist and biologist with an unwavering passion for birds and wild animals.
Dr. Wilson’s journey in ornithology began in childhood and led him to obtain a Ph.D. in Ornithology from the prestigious Avian Research Institute. He has worked closely with renowned experts in the field and conducted extensive research and field studies globally.

